Deploying a Django Application Using Gunicorn and Nginx
Leave a comment on Deploying a Django Application Using Gunicorn and Nginx
Deploying a Django application for production requires a robust and scalable setup. This tutorial will demonstrate how to deploy a Django application with Nginx serving as the reverse proxy and Gunicorn as the WSGI server. This combination guarantees load balancing, better performance, and effective request handling.

Prerequisites
Before proceeding, ensure you have the following:
- A server running Linux-based distribution server (Here we use an Ubuntu 22.04 server)
- Python 3 and pip installed
- A Django application ready for deployment
- Nginx installed on the server
- A virtual environment set up for your Django project
Step 1 – Install Gunicorn
Gunicorn is an effective Python WSGI HTTP server for your Django application.
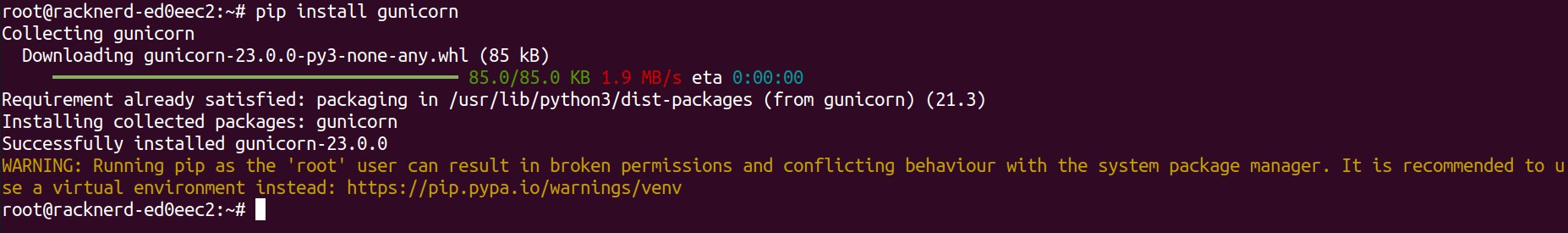
pip install gunicornAfter installation, navigate to your Django project directory and test Gunicorn:
gunicorn --bind 0.0.0.0:8000 myproject.wsgi:application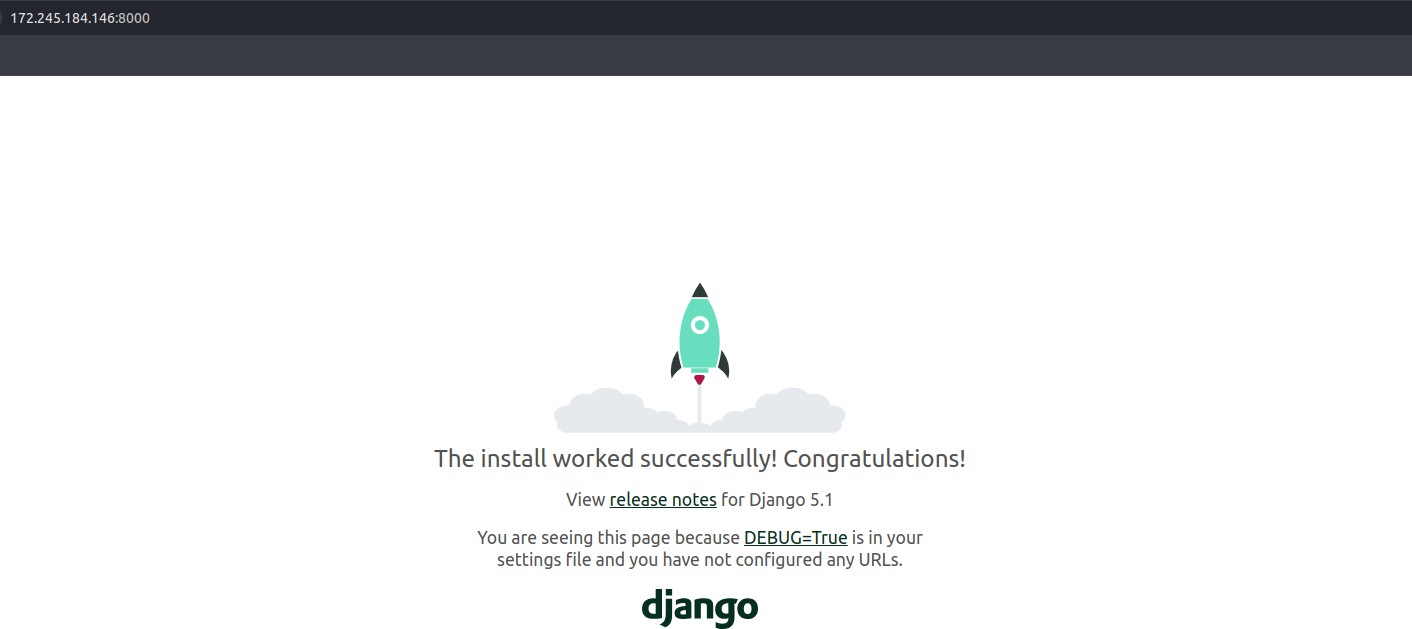 This command runs Gunicorn on port 8000 and serves your Django application. Verify the working by accessing http://your-server-ip:8000.
This command runs Gunicorn on port 8000 and serves your Django application. Verify the working by accessing http://your-server-ip:8000.
Step 2 – Configure Gunicorn as a Systemd Service
To ensure Gunicorn runs as a background service and restarts automatically on failure, create a systemd service file:
sudo nano /etc/systemd/system/gunicorn.serviceAdd the following content, replacing ‘myuser’ and ‘myproject’ with your details:
[Unit]
Description=Gunicorn instance to serve Django application
After=network.target[Service]
User=myuser
Group=myuser
WorkingDirectory=/home/myuser/myproject
ExecStart=/home/myuser/myproject/venv/bin/gunicorn –workers 3 –bind unix:/home/myuser/myproject/gunicorn.sock myproject.wsgi:application[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
(make sure you choose the right WorkingDirectory and all the other terms.) Save and exit, then reload systemd and start the service:
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
sudo systemctl start gunicorn
sudo systemctl enable gunicornStep 3 – Configure Nginx as a Reverse Proxy
Nginx will handle incoming requests and forward them to Gunicorn.
Create a new Nginx server block:
sudo nano /etc/nginx/sites-available/myprojectAdd the following configuration:
server {
listen 80;
server_name your_domain_or_IP;
location / {
proxy_pass http://unix:/root/myproject/gunicorn.sock;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For
$proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
}
}Enable the configuration and restart Nginx:
sudo ln -s /etc/nginx/sites-available/myproject /etc/nginx/sites-enabled
sudo nginx -t
sudo systemctl restart nginxStep 4 – Adjust Firewall Rules
Ensure the firewall allows HTTP and HTTPS traffic:
sudo ufw allow 'Nginx Full'Step 5 – Verify the Deployment
Visit http://your-domain-or-ip in a browser. Your Django application should now be accessible via Nginx and Gunicorn.
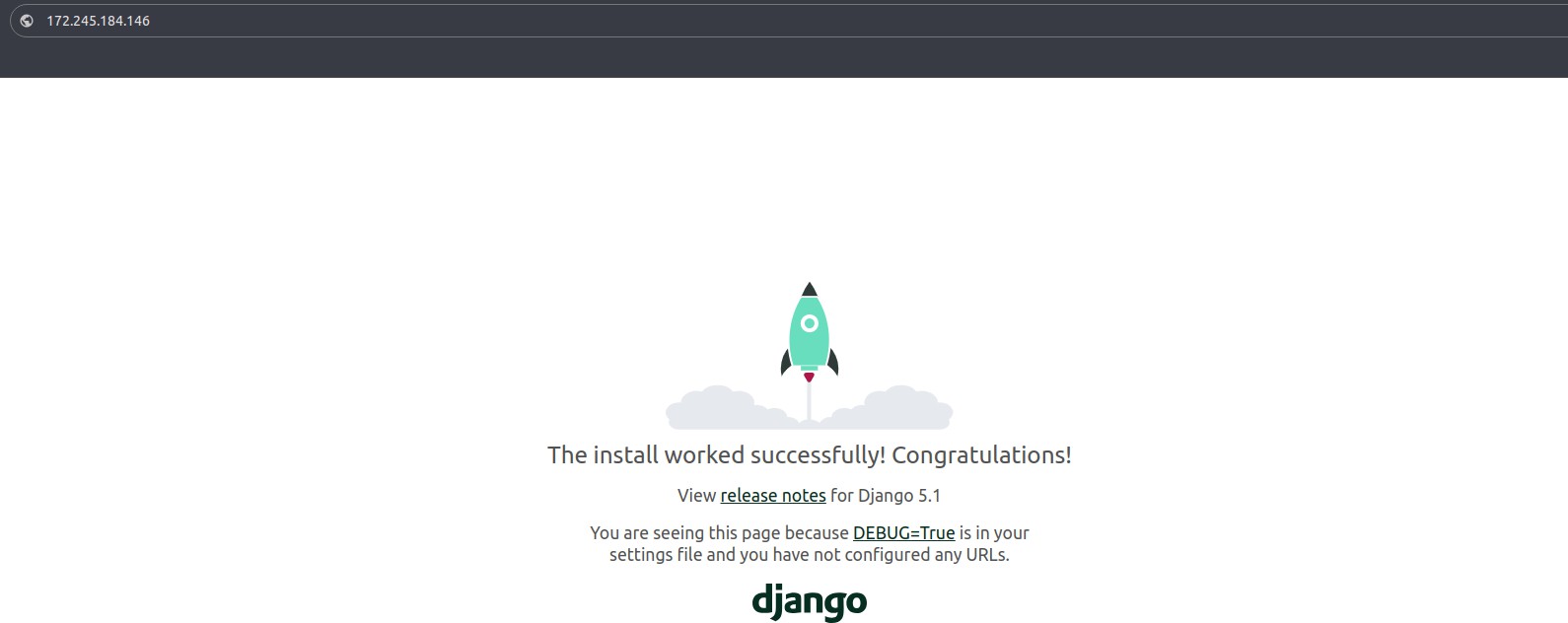
Conclusion
Your Django application can be deployed in a scalable and high-performance manner by combining Gunicorn and Nginx. The application is effectively served by Gunicorn, and Nginx manages load balancing, caching, and incoming requests. With this configuration, your Django project is guaranteed to be production-ready with enhanced security and request handling.
